Fibonacci Retracement: A Guide to Identifying Key Levels
Fibonacci retracement is a popular technical analysis tool used by traders to identify potential support and resistance levels based on the Fibonacci sequence. Named after the Italian mathematician Leonardo Fibonacci, this tool leverages specific ratios derived from the Fibonacci sequence to predict possible price reversals or continuation levels within a trend. Fibonacci retracement is especially useful in trending markets, where it helps traders find entry points, set stop-loss levels, and determine profit targets.
1. What is Fibonacci Retracement?
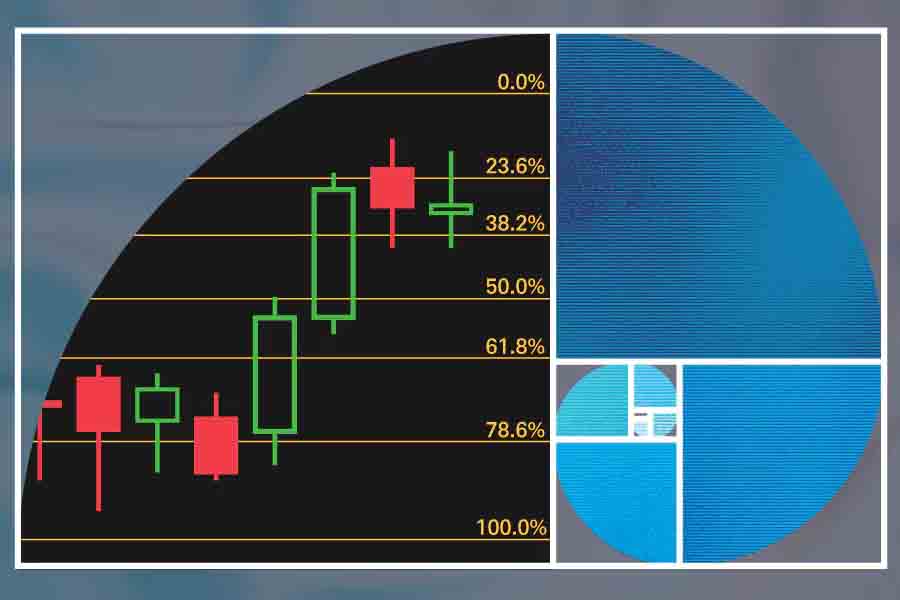
Fibonacci retracement levels are horizontal lines that indicate where support and resistance are likely to occur. These levels are derived from the key Fibonacci ratios: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%. Each ratio represents a potential point of retracement within a price trend, indicating where the price might pause or reverse.
The 50% level, although not technically a Fibonacci ratio, is often included because it represents the halfway point of a price move and is a psychologically significant level for many traders.
2. Understanding Fibonacci Ratios
The Fibonacci ratios used in technical analysis are derived from the Fibonacci sequence, a series of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones (e.g., 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, etc.). The key ratios are calculated by dividing one number in the series by another:
- 23.6%: Calculated by dividing a number by the number three places to its right (e.g., 8 ÷ 34 = 0.236).
- 38.2%: Calculated by dividing a number by the number two places to its right (e.g., 21 ÷ 55 = 0.382).
- 61.8%: Known as the “golden ratio,” calculated by dividing a number by the next number to its right (e.g., 34 ÷ 55 = 0.618).
- 78.6%: The square root of 61.8%, representing a deeper retracement level.
These ratios are plotted on a price chart to identify potential support and resistance levels, providing traders with an edge in predicting where the price might reverse.

3. How to Use Fibonacci Retracement in Trading
Fibonacci retracement is typically applied to identify potential support or resistance levels during a retracement within a trend. It is drawn between two significant price points, usually a swing high and a swing low, and the retracement levels are plotted horizontally at key Fibonacci ratios.
- Drawing Fibonacci Retracement:
- Identify a significant price movement in the market (either an uptrend or downtrend).
- Select the Fibonacci retracement tool on your charting platform.
- Click at the start of the price movement (swing low in an uptrend or swing high in a downtrend).
- Drag the tool to the end of the price movement (swing high in an uptrend or swing low in a downtrend).
- The Fibonacci retracement levels (23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%) will be plotted on the chart.
- Using Fibonacci Retracement for Trading:
- Support and Resistance Levels: Each Fibonacci retracement level can act as support or resistance. In an uptrend, traders expect the price to retrace to one of the Fibonacci levels and then bounce back up, using these levels as potential entry points for long positions. In a downtrend, traders look for the price to retrace upwards to a Fibonacci level before continuing downwards.
- Entry and Exit Points: Traders can use Fibonacci retracement levels to set entry points during retracements, expecting the trend to continue after testing a key level. Conversely, traders can set profit targets at Fibonacci levels when trading against the trend.
- Stop-Loss Placement: Traders often place stop-loss orders just beyond the Fibonacci levels to minimize losses in case the price moves against their positions.
4. Fibonacci Retracement Levels in Uptrends and Downtrends
The interpretation of Fibonacci retracement levels varies depending on whether the market is in an uptrend or a downtrend:
- Fibonacci Retracement in an Uptrend: In an uptrend, Fibonacci retracement levels act as potential support areas where the price might pause or reverse before continuing higher. Traders look for retracement levels like 38.2%, 50%, or 61.8% as potential entry points for long positions.
- Example: Suppose a stock price rises from $100 to $150 and then starts to pull back. Applying Fibonacci retracement from $100 (swing low) to $150 (swing high), the retracement levels would be calculated as follows:
- 23.6% level: $138.20
- 38.2% level: $130.90
- 50% level: $125.00
- 61.8% level: $119.10
Traders might look for a reversal at one of these levels to continue the uptrend.
- Example: Suppose a stock price rises from $100 to $150 and then starts to pull back. Applying Fibonacci retracement from $100 (swing low) to $150 (swing high), the retracement levels would be calculated as follows:

- Fibonacci Retracement in a Downtrend: In a downtrend, Fibonacci retracement levels act as potential resistance areas where the price might pause or reverse before continuing lower. Traders look for retracement levels like 38.2%, 50%, or 61.8% as potential entry points for short positions.
- Example: Suppose a stock price drops from $200 to $100 and then starts to retrace upwards. Applying Fibonacci retracement from $200 (swing high) to $100 (swing low), the retracement levels would be:
- 23.6% level: $123.60
- 38.2% level: $138.20
- 50% level: $150.00
- 61.8% level: $161.80
Traders might look for the price to reverse at one of these levels to continue the downtrend.
- Example: Suppose a stock price drops from $200 to $100 and then starts to retrace upwards. Applying Fibonacci retracement from $200 (swing high) to $100 (swing low), the retracement levels would be:
5. Trading Strategies Using Fibonacci Retracement
There are several strategies that traders use with Fibonacci retracement levels:
- Fibonacci Retracement and Trendline Confluence: Combine Fibonacci retracement levels with trendlines to identify strong support or resistance zones. If a Fibonacci level aligns with a trendline, it increases the likelihood of a price reversal.
- Fibonacci Retracement and Candlestick Patterns: Look for candlestick reversal patterns, such as hammer, engulfing, or doji, at Fibonacci retracement levels to confirm a potential price reversal.
- Fibonacci Retracement and Moving Averages: Use Fibonacci levels in conjunction with moving averages (e.g., 50-day or 200-day moving averages) to identify potential entry points. If a Fibonacci level coincides with a moving average, it adds strength to the level as support or resistance.
- Fibonacci Retracement and RSI/MACD: Combine Fibonacci retracement levels with momentum indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) to confirm overbought or oversold conditions at key retracement levels.
6. Limitations of Fibonacci Retracement
While Fibonacci retracement is a powerful tool, it has some limitations:
- Subjectivity: The effectiveness of Fibonacci retracement depends on correctly identifying the swing high and swing low points. Traders may choose different points, leading to varying retracement levels.
- Not Always Accurate: Fibonacci levels are not always precise support or resistance levels. The price may briefly penetrate or overshoot these levels before reversing, leading to false signals.
- Requires Confirmation: Fibonacci retracement levels should not be used in isolation. They are more effective when combined with other technical indicators, patterns, or analysis methods for confirmation.
- Not Predictive of Direction: Fibonacci retracement only indicates potential reversal levels, not the direction of the overall trend. Traders must consider the broader trend context when using this tool.

7. Best Practices for Using Fibonacci Retracement
To maximize the effectiveness of Fibonacci retracement:
- Use Higher Timeframes: Apply Fibonacci retracement on higher timeframes (e.g., daily or weekly charts) to identify stronger support and resistance levels.
- Combine with Other Indicators: Use Fibonacci retracement in conjunction with other technical indicators, such as trendlines, moving averages, or volume analysis, to confirm signals.
- Wait for Confirmation: Do not enter trades solely based on Fibonacci retracement levels. Wait for price action or indicator confirmation before making trading decisions.
8. Conclusion
Fibonacci retracement is a versatile and powerful tool that helps traders identify potential support and resistance levels during a trend. By applying Fibonacci levels to significant price movements, traders can anticipate areas where the price might reverse or consolidate, providing valuable insights for entry, exit, and stop-loss placement. While Fibonacci retracement is not foolproof, combining it with other technical analysis tools and strategies can enhance its effectiveness and improve trading outcomes.